Whether renting or buying it is certainly getting dearer to get a roof over our heads. The reason is simple. House prices are growing faster than incomes. In colder mathematical terms international surveys leave little doubt that housing in Australia is unaffordable.
Demographia found Australia the least affordable of the six western countries it surveyed (Australia, New Zealand, United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Ireland) in both 2007 and 2009. In 2009, for example, it listed all capital cities in Australia as “severely unaffordable” (the worst category). No Australian city was “affordable”. The measure used was the Median Multiple Test: the number of years of the median household income it takes to buy the median priced home. At 9.6 the Sunshine Coast had the dubious distinction of being the worst of the “severely unaffordable” areas. The Gold Coast was little better.
Overall, Queensland was mentioned no less than nine times in the 60 least affordable markets. Table 1 shows where each of the capital cities stood in 2007 (at the height of the “housing bubble”) and in 2009.
Advertisement
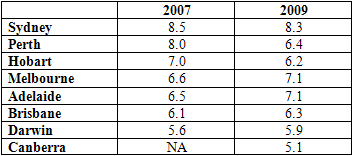
Table 1: Median multiples for Australian capital cities
(Severely unaffordable” refers to a Median Multiple of 5.1 and over. A Median Multiple of 3 is taken to be “affordable”.)
Yet the picture is worse than this. For one thing the median household income is now usually two incomes. Then again there is the effect of interest charges. For example, an affordable house bought in 2007 at a Median Multiple of 5 with interest of 6.5 per cent over 30 years was really equivalent to buying a house with a Median Multiple of 12 (2007, p.13).
Changing terminology
Despite its persistence no progress has been made in improving housing affordability. One thing that makes it more difficult is the incorrect terminology.
The best way to begin to understand the problem is to compare the least affordable and the most affordable places in Australia. Mosman in Sydney and Cottesloe in Perth may well be the least affordable places in Australia. Each has a median house price of about $2 million. By contrast, the most affordable place in Australia is the municipality of Central Darling in far western New South Wales. Its median house price is $39,000. To put it bluntly, waterside Mosman and Cottesloe, lying between the CBD and the beaches, enjoy the best that nature and society have to offer, the other has almost the worst.
Advertisement
Very simply, the difference is location. This suggests that, if we truly wanted to understand the problem, we should replace housing unaffordability by land unaffordability. Housing construction costs are not the problem. Land price is the problem.
The land price cycle
Some say that you can set your investment clock by an 18-year cycle: four years to adjust to one “bust”, followed by seven years of moderate growth and then seven more years of frantic speculation. Near the end the wise investor “cashes up” and takes a holiday!
How this speculation typically works was let slip by a local real estate agent when it was rumoured that Alcoa would soon be moving into Portland, Victoria in 1980. He wrote “people just went mad and there was huge land activity for weeks … Speculators bought up big and investors …pulled their properties off the market to wait for higher prices. Three hundred blocks of land … were immediately withdrawn from the market as the demand increased”.
Note that supply is reduced as demand increases. Little wonder then why there is a price “bubble”! Demographia reported that, between 1993 and 2006 land prices in Australia rose about 220 per cent.
In a rapidly rising market lending regulations are relaxed. Banks think it is safe to lend. Borrowers think it is safe to borrow. Thus, acquisitions are largely financed by debt. One US bank lent to a man who claimed a six-figure income as a Mariachi singer. The only proof he gave was a photo of himself outside his house dressed in a Mariachi uniform! In the United States, especially, we see the advent of sub-prime mortgages as the poor join in the speculation, and the dangers are compounded by the sale of these mortgages, packaged as bonds, all over the world.
Interest rates rise. Investors begin to drive first home-buyers out of the market. In 2005 The Age reported that the OECD found Australia had the most over-priced housing in the world. Its prices were 52 per cent higher than were justified by the rents. Naturally, in such a situation it was more profitable to pursue capital gains from established housing than to build new accommodation for rental income. With so much money being poured into speculation rising land prices and interest rates soon began to impede both housing construction and new business construction.
Ultimately of course everything depended not on the exchange of paper titles but on the health of what is now called the “real” economy. Warning signs began to appear on the stock market. Greed turned to fear. Credit was frozen. Many who financed their acquisitions from debt suddenly found themselves unable either to borrow more money or to pay off mounting interest bills. Panic selling replaced panic buying. Bankruptcies and foreclosures rapidly increased. There was recession.
Civilising greed
It is easy to dismiss what happened as simply greed that may be tamed by more rigorous regulation - something that is said after every recession. Note the assumption. The institutions are fine but those who operate them are prone to mistakes caused by greed. Yet, clearly, something more than this is wrong.
But it is plausible to suggest that the essence of the problem is greed. Greed is certainly there. Greed manifests as a kind of panic buying prompted by the possibility of getting something for nothing, and getting it before someone else gets it. Speculation answers one of our deepest urges which is to achieve something with the least effort. Rigorous regulation does nothing to take away that urge; it is merely an attempt to stop it by force.
As soon as the period of adjustment to one recession ends a period of moderate economic growth begins and land values begin to recover. Inevitably, these land values are capitalised into land prices. Thus, in tandem with economic expansion there is a growth of land prices. There lies the possibility of something for nothing. Speculation is then inevitable. This is not a one-off speculation like the South Sea Bubble or the Dutch Tulip mania. It is a regularly occurring phenomenon.
Force does not civilise greed; force merely tries to contain it. Greed is civilised when the activity is radically altered from a competitive into a co-operative activity.
Political v private economy
The answer lies in seeing the difference between land value and land price. Land value arises from social progress. Only what enhances that progress is truly part of the economy - what classical economists called the political economy. Land price plainly does not enhance social progress. It is not part of the public economy. It arises out social progress but in time it impedes it.
We have seen what it does. Another test is to subject land price to the test of ethics. Land price is what happens to land value when it is privatised and sold. It is some multiple of land value. (That in itself makes buying a house harder.) Yet land value does not arise from individual effort. It arises from natural and social advantages that surround land. While as John Stuart Mill says somewhere “landlords grow richer in their sleep”, the value of land emanates elsewhere in the presence and activities of the community.
Economists assume that all is right with the economy except for occasional greed; in fact, something quite plainly is rotten. It is not the privatisation of land; it is the privatisation of land value.
Conclusion
The point of view given here has drawn heavily on the theory of industrial depressions given in Progress and Poverty by the American social philosopher and economist Henry George (1839-1897). Land value, George argued, was public property. As the largest value we have George postulated that a “single tax” on that value should replace the taxation of labour and capital.
While other causes from time to time exacerbate “housing” unaffordability the key reason for “housing” unaffordability is that land prices are growing faster than incomes. The graph below shows this:
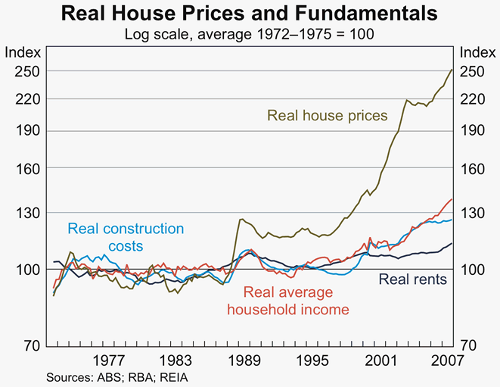
Kavanagh (2009)
While land scarcity and speculation periodically cause land “bubbles” George argued that the inexorable growth of land values with social progress must in the end outpace the growth of individual incomes. This poses a Sphinx-like question for our civilisation. Housing unaffordability is the most obvious sign of that question.