A longer term problem, though, is that world wheat production has not been growing to keep up with growing world population. Part of this lack of growth may be competition from biofuels. Part of the lack of growth also relates to the fact that the “green revolution” improvements (adding irrigation and fertilizer) are mostly behind us. While irrigation and fertilizer greatly improved production at the time of the change, gains in production since 1990 have been much smaller.
The cost of imported food, particularly wheat, has risen, partly because of the relatively smaller harvest, and partly because the cost of production and transport is rising because of rising oil prices. Figure 5 shows the close relationship food prices and oil prices. The Food Price Index used in this graph is the FAO’s Food Price Index related to food for export; Brent oil prices are spot prices from the EIA.
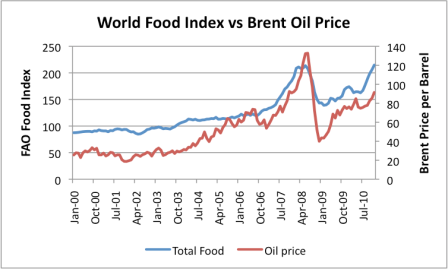
Figure 5. World food price trend is similar to Brent oil price trend.
Advertisement
With oil prices higher now (because world production is close to flat, and as countries come out of recession, they want more), food prices of all types are higher as well. Oil is used directly in the production of grain and indirectly in storage and transit, so its cost becomes important.
The higher food prices contribute to the overall inflation problem that Egypt already had. In 2010, the CIA Factbook estimated the inflation rate to be 12.8%. Since wages don’t always rise to match inflation rates, inflationary pressures have no doubt put more pressure on the government to increase subsidies, at a time it cannot really afford to do so.
Impact on the Rest of the World
Why does everyone else respond so strongly to Egypt’s problems?
One reason is that other Arab countries are also feeling some of the same pressures. Food prices are rising everywhere. Many low income people spend in excess of 50% of their income for food, so a rise in food costs becomes a real issue. People have come to depend on oil and food subsidies. If they are taken away, or not raised sufficiently to compensate for the higher costs of imports, it is a real problem.
Oil prices seem to be affected as well. If the Suez Canal should be closed because of disruptions, it could affect oil transit, particularly to Europe. According to the EIA:
Advertisement
An estimated 1.0 million bbl/d of crude oil and refined petroleum products flowed northbound through the Suez Canal to the Mediterranean Sea in 2009, while 0.8 million bbl/d travelled southbound into the Red Sea.
The amounts being transported through the Suez canal are now likely down a little from these amounts in 2011, because of reduced imports/exports worldwide, but they are still substantial. Europe’s oil imports are about 10 million barrels a day of oil, according toEnergy Export Data Browser (using BP’s data). If all of the amounts that flowed northbound went to Europe, they would amount to about 10% of Europe’s imports, or about 7% of Europe’s consumption. In fact, some of these exports go farther–in particular to the US, or to Canada, so the amount in question is probably lower than this relative to Europe’s consumption, say 4% or 5%. But even a small shortfall is a problem, in a world that needs oil for transport, food production, heating, and many other uses.
The inability to send products southbound through the Suez Canal is likely to also be a problem. Part of what Europe does is refine oil, keep the products it needs, and send other products to customers elsewhere. The whole system is set up assuming close to “just-in-time” production and delivery. While there is some storage capability, after a few days or weeks the system is likely to start running into problems. Those in need of the refined products being sent southward through the Suez Canal will be in need of them, and Europe will have excess supply. Of course, it is possible to use longer shipping routes, but this uses more oil for shipping and takes longer, so is more expensive. There is also a time-delay when the new system is put in place.
All of these problems (relating to both north and south-bound oil traveling through the Suez) can be worked around, but there could be a period of disruption for a while, as supplies begin traveling a longer route.
Discuss in our Forums
See what other readers are saying about this article!
Click here to read & post comments.
31 posts so far.